Gums hold our teeth in place. But what if your gums are infected? Have you ever thought about it? You might not even know that your gums are infected. That’s why, through this article, we aim to create awareness about gum disease.
DID YOU KNOW
Nearly half of the adults aged 30 and older have some form of gum disease. Yet, most don’t realise it until it’s too late!
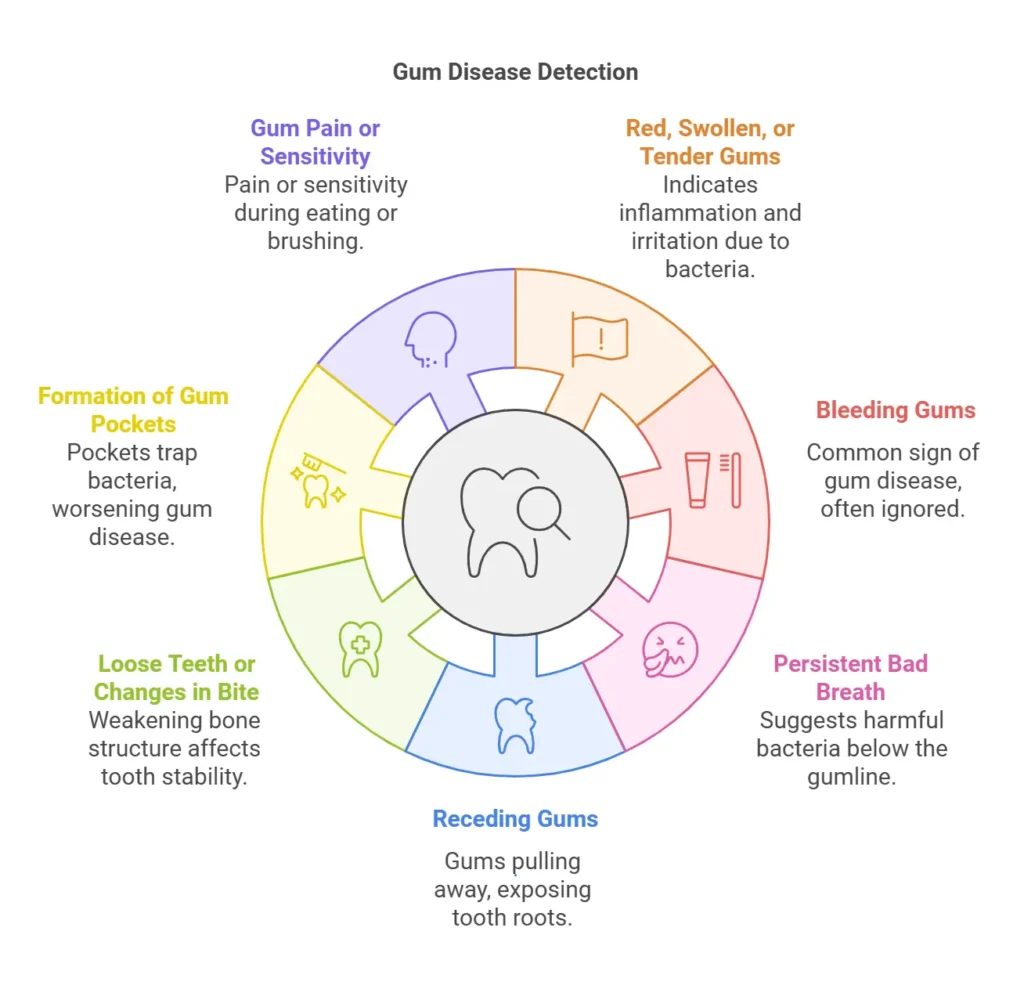
One of the earliest signs of gum disease is inflammation. As a rule of thumb, if your gums look redder than usual or feel swollen and tender when touched, it’s a signal that bacteria are irritating your gum tissue. Healthy gums are typically firm and pink, so any changes in their appearance should be taken seriously.
Do your gums bleed when you brush or floss? This is one of the most common and often ignored signs of gum disease. Bleeding gums indicate inflamation in gums, which is an early symptom of gingivitis—the first stage of gum disease.
Bad breath, or halitosis, that doesn’t go away even after brushing and rinsing could be more than just a nuisance. It might indicate harmful bacteria thriving below the gumline, leading to infection.
If your teeth appear longer than usual, it’s not because they’re growing—it’s because your gums are pulling away. Gum recession is a clear sign that gum disease is progressing. Left untreated, it can expose the roots of your teeth and lead to sensitivity or decay.
When gum disease advances, the supporting bone structure that holds your teeth in place can weaken. This may cause your teeth to feel loose or shift. You might also notice changes in the way your teeth come together when you bite.
A significant sign of gum disease is the formation of pockets between your teeth and gums. These pockets trap bacteria, food particles, and plaque, which can worsen the condition. Dentists use this as a key diagnostic tool to determine the severity of gum disease.
If your gums hurt when eating, drinking, or brushing, this could indicate an infection or irritation caused by gum disease. Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods may also accompany this pain.
Gum disease isn’t just about your oral health; it’s linked to systemic issues such as heart disease, diabetes, and even respiratory problems. Spotting and addressing these signs early can prevent them from progressing into more severe stages that require extensive treatment.
Gum redness, swelling, or tenderness can result from various causes. Brushing too hard, hormonal changes or certain medications can cause gum redness.
But there is a difference when this redness is caused due to other factors vis-a-vis gum disease.
Here are some things you should keep in mind to determine if you have a gum infection.
Now that you know the exact symptoms of gum disease, let us now turn our attention to the fact about different stages of gum disease, prevention and simple home remedies.
Gum disease progresses in three main stages, starting with gingivitis, the earliest and most treatable phase. At this stage, symptoms like red, swollen, or bleeding gums may appear due to plaque buildup.
If untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. It is a stage where the infection spreads below the gum line, damaging the bone and tissues supporting the teeth.
In its most severe form, advanced periodontitis, extensive bone loss occurs, causing loose teeth, gum recession, and even tooth loss.
Early detection and treatment of gum issues can help to prevent gum disease from reaching these advanced stages.
Gum disease can begin from mild discomfort and turn to a serious condition that impacts both your oral and overall health. Recognizing the signs of advanced gum disease and understanding the associated risks is crucial for timely intervention.
Advanced gum disease, or periodontitis, presents clear warning signs:
If you experience these symptoms, your gum disease is likely in its advanced stage and requires a dentist.
Understanding the difference between gum pain and tooth pain can help you address the root issue effectively:
If the pain is accompanied by redness and swelling of the gums, it’s more likely gum disease. However, pain that is sensitive to pressure or temperature might indicate a tooth issue.
Without treatment, gum disease can lead to gum abscesses—painful pockets of pus caused by severe bacterial infections. Abscesses cause discomfort and can spread the infection to surrounding tissues and bone.
If the supporting bone and tissue weaken, teeth may loosen or fall out. Tooth loss isn’t just a cosmetic concern; it can affect your bite, speech, and overall oral health.
Your gum disease is serious if you notice symptoms like receding gums, persistent pain, pus, loose teeth, or gum abscesses. A dentist can confirm the severity through an examination and X-rays.
Gum disease becomes irreversible when it progresses to advanced periodontitis. At this stage, bone and tissue loss occurs, and while it can be managed, the damage cannot be undone.
The progression of gum disease varies depending on factors like oral hygiene, diet, and genetics. Without treatment, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis within months, leading to severe complications.
Stopping gum disease in its tracks requires a combination of consistent oral hygiene, professional care, and lifestyle adjustments.
Daily oral care is the first line of defense against gum disease.
Consistency with these practices can prevent the progression of gingivitis into more severe forms of gum disease.
Professional dental care is crucial for preventing gum disease from advancing.
Visit your dentist every six months or more frequently if you are at higher risk for gum disease.
Your diet plays a significant role in gum health by providing essential nutrients for tissue repair and immune function.
Avoid sugary foods and beverages, as they fuel bacteria that contribute to plaque formation.
Gingivitis can be reversed with proper oral hygiene and professional cleanings in its early stages. However, once it progresses to periodontitis, the damage is permanent, and only management, not repair, is possible.
While receding gums cannot regenerate fully, maintaining good oral hygiene, eating a nutrient-rich diet, and using natural remedies like oil pulling can support gum health and reduce inflammation.
Toothpastes with fluoride, antibacterial agents like triclosan, or natural ingredients like aloe vera can help combat gum disease. Look for products specifically designed for gum health, such as those labelled for treating gingivitis or reducing plaque.
Gum disease can often start mild but quickly escalate if not addressed. While professional care is essential for advanced stages, home remedies can play a role in managing or even reversing gum disease in its early stages. Let’s explore effective home remedies, professional treatments, and when it’s time to see a dentist.
Saltwater rinses are a simple, affordable, and effective way to care for your gums.
While salt water can’t cure advanced gum disease, it’s an excellent supportive measure for minor gum inflammation.
Natural remedies like oil pulling and natural antibiotics are popular for managing gum health, but do they live up to the hype?
Natural remedies can help in early stages or as part of a broader oral hygiene routine, but they are not a replacement for professional care.
Home remedies are useful for maintaining gum health, but they have their limits. It’s crucial to visit a dentist if:
Professional Treatments:
Early-stage gum disease (gingivitis) can be reversed with daily brushing, flossing, rinsing with salt water, and a healthy diet. Regular use of antimicrobial mouthwashes and natural remedies like oil pulling can also help.
Saltwater can soothe gums, reduce swelling, and flush out bacteria, but it can’t fully heal an infection. Persistent infections need professional evaluation and treatment.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to visit your dentist promptly. A professional can assess your gums, recommend the right treatment, and help you maintain your oral health. Don’t wait until it’s too late—your gums deserve as much attention as your teeth!
By staying vigilant and proactive, you can keep gum disease at bay and enjoy a healthier smile.